[yolov3学习记录3]用自己的数据集训练
参考博客:从零开始带你一步一步使用YOLOv3训练自己的数据_红色石头的专栏-CSDN博客_yolov3训练自己的数据集
首先按照VOC2007数据集的格式创建好文件夹储存数据。
Annotations储存xml标签问文件,ImageSets刚开始是个空文件夹,里面有个Main子文件夹用于储存test.txt train.txt val.txt trainval.txt这种数据分类文件。JPEGImages用于储存图片数据。
刚开始,师兄给的数据如图。各科的标签是分开的,且是txt格式。而图片存在question文件夹。而里面的txt如下:
83,106,1121,106,1121,405,83,405
共8个数据,每两个代表一个坐标,8个代表了图片框选位置的左上角 右上角 左下角 右下角。而多个框则多行。

而如“学习报告-2”里面写的,VOC数据集的txt标签格式和这个有出入,那么要转换成VOC的txt格式,则是通过xml这个媒介。也就是先把xml和对应的图片放进那个VOCdevkit/VOC2007里面的2个文件夹先。
此时,先用txt2xml.py转txt标签为xml标签。(要改标签名为“question”)
#coding=UTF-8
# Created: 210331 9:56
# Last edited: 210331 9:56
#将标注数据的txt标签转化为xml格式
import os
import xml.dom.minidom as xmldom
import cv2
input_dir = './210506/english_label/'
output_dir = './Question/Label/'
img_dir = './210506/question/'
LabelName = 'question'
file_list = os.listdir(input_dir)
for file in file_list:
if file[-4:] != '.txt':
continue
with open(input_dir + file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
img_path = file[:-4] + '.png'
img = cv2.imread(img_dir + img_path)#图片地址
[height, width, depth] = img.shape#保存图片信息
doc = xmldom.Document()
root = doc.createElement("annotation")
doc.appendChild(root)
nodeFolder = doc.createElement('folder')
nodeFolder.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('input_images'))
root.appendChild(nodeFolder)
nodeFilename = doc.createElement('filename')
nodeFilename.appendChild(doc.createTextNode( img_dir + file[:-4] + '.png'))
root.appendChild(nodeFilename)
nodeSource = doc.createElement('source')
nodeDatabase = doc.createElement('database')
nodeDatabase.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('Unknown'))
nodeSource.appendChild(nodeDatabase)
root.appendChild(nodeSource)
nodeSize = doc.createElement('size')
nodeWidth = doc.createElement('width')
nodeWidth.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(width)))
nodeHeight = doc.createElement('height')
nodeHeight.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(height)))
nodeDepth = doc.createElement('depth')
nodeDepth.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(depth)))
nodeSize.appendChild(nodeWidth)
nodeSize.appendChild(nodeHeight)
nodeSize.appendChild(nodeDepth)
root.appendChild(nodeSize)
nodeSegmented = doc.createElement('segmented')
nodeSegmented.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
root.appendChild(nodeSegmented)
for line in lines:
data = line.split(',')
nodeObject = doc.createElement('object')
nodeName = doc.createElement('name')
nodeName.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(LabelName))
nodePose = doc.createElement('pose')
nodePose.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
nodeTruncated = doc.createElement('truncated')
nodeTruncated.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
nodeDifficult = doc.createElement('difficult')
nodeDifficult.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
nodeBndbox = doc.createElement('bndbox')
nodeXmin = doc.createElement('xmin')
nodeXmin.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(data[0])))
nodeBndbox.appendChild(nodeXmin)
nodeYmin = doc.createElement('ymin')
nodeYmin.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(data[1])))
nodeBndbox.appendChild(nodeYmin)
nodeXmax = doc.createElement('xmax')
nodeXmax.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(data[2])))
nodeBndbox.appendChild(nodeXmax)
nodeYmax = doc.createElement('ymax')
nodeYmax.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(data[5])))
nodeBndbox.appendChild(nodeYmax)
nodeObject.appendChild(nodeName)
nodeObject.appendChild(nodePose)
nodeObject.appendChild(nodeTruncated)
nodeObject.appendChild(nodeDifficult)
nodeObject.appendChild(nodeBndbox)
root.appendChild(nodeObject)
with open(output_dir + file[:-4] + '.xml', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
doc.writexml(fp, indent='\t', addindent='\t', newl='\n', encoding='utf-8')
再放进去一部分xml文件。然后自己写了个python脚本,遍历文件夹,然后从指定文件夹中选取同名图片到指定文件夹中。
源码如下:
# coding = UTF-8
import os
import shutil
def CopyFile(fromfile,topath): # 复制函数
if not os.path.isfile(fromfile):
print ("%s not exist!"%(fromfile))
else:
fpath,fname=os.path.split(fromfile) # 分离文件名和路径
if not os.path.exists(topath):
os.makedirs(topath) # 创建路径
shutil.copy(fromfile, topath + fname) # 复制文件
#print ("copy %s -> %s"%(fromfile, topath + fname))
loc_labeldir = '/data/hwj/darknet/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/'
loc_imagedir = './210506/question/'
loc_to_imagedir = '/data/hwj/darknet/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/'
type_photo = '.png'
#读取label文件夹内容
label_file_list = os.listdir(loc_labeldir)
for label_file in label_file_list:
if label_file[-4:] != '.xml':
continue
#print('here')
CopyFile(loc_imagedir+label_file[:-4]+type_photo,loc_to_imagedir)
这样便可得到相应的图片和标签了。
然后运行参考博客中原作者给出的test.py
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.8
train_percent = 0.8
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
将数据分类成test train val trainval几类。
此时,经过这几项操作,我们已经得到一个标准的VOC2007数据集了,便可以按照之前官网VOC数据集的操作来搞。用VOC_label.py来把xml标签转成VOC的txt且在darknet根目录分出test train val trainval。然后用下面的命令进行合并。
cat 2007_train.txt 2007_val.txt > train.txt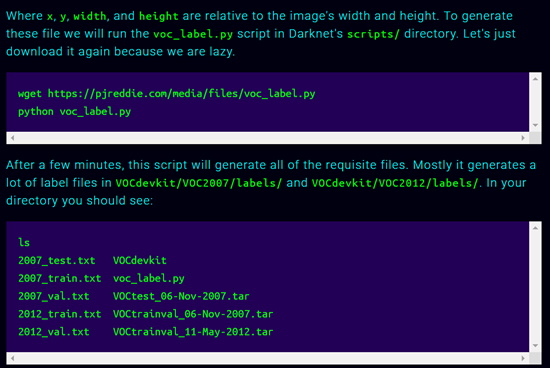
不过VOC_label.py里面的源码还要微修,因为我们只有VOC2007,而官网例子有2007 2012两个版本的数据,此外,我们只有一个叫“question”的类,而官网例子有20个。
以上操作完成后,开始挑yolo的配置。
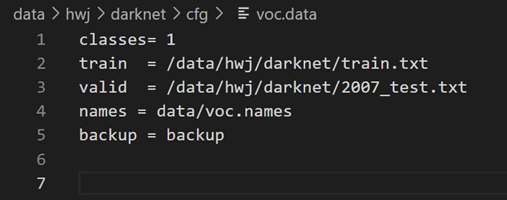
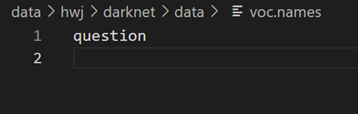
当然,还有cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg。参数 filters 由下式计算:3*(5+classes),例如本例中 classs=4,则filters=27;参数 class 改为实际的类别个数;
最后就可以开始训练了。一开始训练是训练一会儿就会提示Segmentation fault (core dumped)
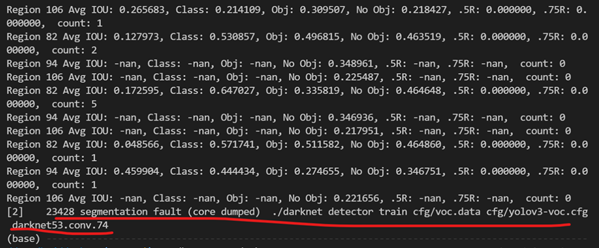
这个问题搞了好久,一开始以为是配置的问题,到处改,但还是报错,最后是按师兄说的,减少数据到了175(原来是4275),排除了这个问题。初步判断是某张图片或者标签有问题,导致用到问题标签或图片的时候报错。
训练完后,获得backup/yolov3-voc.backup这个权重文件。用它来判断的时候,却出现了可以判断题图在哪,却不能正确出标签文字的问题。如下:
无论怎么样都是错误的标签文本,和之前官网那个例子一样。
最后通过修改cfg/coco.names才搞定的,刚开始以为我们用VOC的训练集,只需要改VOC的配置就行了,以为和COCO无关,现在也不知道为什么要改coco.names,反正改了之后就可以了。如下: